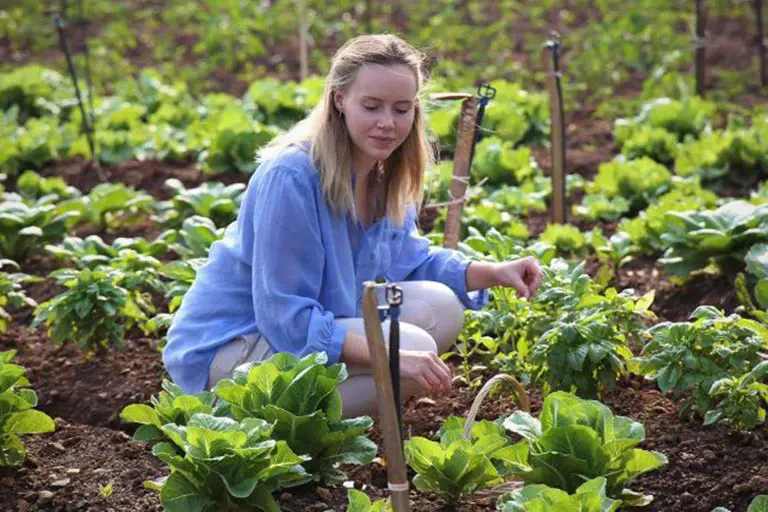
In a farmer’s market or vegetable shop, have you ever been greeted with signs that say “Certified Organic” in bold letters? Have you wondered why they are more expensive than their non-organic counterparts?
Organic fruits and vegetables are increasingly finding their place in the farmer’s market in recent times, as consumers continue their search for chemical-free food and products. Today, when it comes to food production, organic farming is widely considered to be a far more sustainable alternative to conventional farming, amidst climate change, depletion of natural resources, and increased prevalence of lifestyle diseases.
In organic farming, the lack of pesticides and other chemicals improves biodiversity and results in enhanced soil quality and reduced pollution from pesticide or fertilizer run-off. Moreover, consumers are gradually shifting towards organic food consumption, due to growing concerns about the health impacts of accidentally consuming chemical fertilizers and pesticides or their residue in fruits and vegetables.
The Origin and Timeline of Organic Farming
In the early 20th century, the mechanisation of agriculture drastically increased crop yields and made farming more affordable. However, the overexploitation of arable land and water resources along with the use of chemical fertilisers and pesticides resulted in soil erosion and depletion, reduced food quality, and a lack of crop varieties. These negative environmental effects influenced the beginning of the organic farming movement.
What are the Two Types of Organic Farming?
Organic agriculture involves low-input farming which means using only natural resources of nutrients such as manure, crop residues, and compost along with natural methods of crop and weed control rather than synthetic agrochemicals. There are two types of organic farming.
- Pure Organic Farming: In this type of organic farming, farmers use only manures and bio-pesticides with the complete avoidance of inorganic chemicals and pesticides. The farmer also needs to ensure the land has never been exposed to these chemicals. In certain cases, due to the lack of resources required for conventional high-input intensive agriculture, farmers practice pure organic farming as a tradition.
- Integrated Organic Farming: This type of organic farming involves the combination of nutrient management and integrated pest management. It is a cyclical, zero-waste process, where waste products from one process are used as nutrients for other processes. Crop development from natural resources produces the complete nutritive value that prevents the plants from pest and weed infestations.
A Look into the Five Benefits of Organic Farming
Considering the timeline of organic farming, the push toward this farming method – fewer chemicals, better soil management, and more biodynamic methods – isn’t new. Today, organic farming is more of a return to an efficient and environment-friendly farming method, with advanced machinery and equipment, a streamlined supply chain, and the advantages of modern marketing and retailing. Here are five important organic farming benefits.
- Puts greater emphasis on the “natural” factor
Organic agriculture works in harmony with nature by assisting the natural process of farming or plant cultivation, helping it to be a self-sustaining ecosystem. In any agrarian activity, the input and output have to be purely natural. Unlike modern farming methods that focus on quantity and high yield, organic farming focuses on high crop quality and nature-based produce.
- Discourages the use of high-cost agrochemicals
Organic farming does not rule out the use of modern tech-driven machines and tools; however, it is against the use of chemical-based agriculture inputs such as chemical fertilisers. Lack of organic matter makes them more prone to droughts that conventional farmers ignore and is increasing problems for future generations. Thus, organic farming does not use chemicals to enhance soil fertility and biological diversity.
- Promotes genetic biodiversity
Crop rotation is one of the most important techniques used in organic farming. It refers to the cultivation of various kinds of crops in the same field based on the season and in a sequential manner. Organic farmers also use traditional and adapted seeds that are more resistant to diseases and resilient to climate stress. This helps support greater genetic diversity.
- Practices long-term sustainability
Organic farming is eco-friendly and sustainable as it does not involve the use of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides. It makes optimum use of scarce resources such as land and water and boosts yield. Moreover, the use of local and readily available agricultural inputs along with high yield results in a high return on investment for the farmers.
- Promises amazing health benefits
Nutrients are another factor boosting the popularity of organic food products. As organic agriculture uses natural fertilisers and other inputs, the crops and methods obtained from such farming methods are nutritionally superior. In integrated organic farming, the livestock and their waste are used as manure. Such practices produce healthy food and keep the food chain healthy for a long period.
Why Organic Farming is the Future?
Consumers’ inclination toward organic food and the ability of farmers to obtain premium prices from being certified organic will continue to push the organic farming trend. In food-secured developed countries, organic farming can serve as one of the significant food producers. The high cost of fertilisers but the presence of land for growing fertility-building crops in some developing countries will also work to the advantage of organic farmers. Visit Fazlani Natures Nest today to take a tour of our organic farm. Contact us to know more.